Source Transformation
In the analysis of electrical circuits it is often necessary to transform a voltage source to current source or a current source to voltage source for simplifying circuit the calculations. For applying source transformation it is necessary that the voltage source mush have a resistance in series with it (practical voltage source) and a current source must have resistance in parallel with it (practical current source). The source transformation cannot be performed
on an ideal voltage source or an ideal current source.
on an ideal voltage source or an ideal current source.
Transformation of voltage source to current source
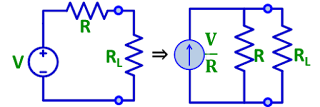 |
| voltage source to current source transformation |
A voltage source of magnitude V in series with its internal resistance R can be transformed to a current source of magnitude V/R in parallel with resistance R as shown in above figure.
Transformation of current source to voltage source
 |
| current source to voltage source transformation |
A current source of magnitude I in parallel with its internal resistance R can be transformed to a voltage source of magnitude I×R in series with the resistance R.
Explanation for source Transformation
From practical voltage source with load resistance RL, the load current obtained is
IL =V/(R+RL)
From practical current source with the same load resistance and internal resistance the load current obtained is
IL=(IR)/(R+RL)
For transformation one source to other it is necessary that the load current obtained in the above two equation must be equal.
By equating the above two equations we obtain,V/(R+RL)=(IR)/(R+RL)
⇒ V=IR or I=V/R

No comments:
Post a Comment